Explain the Differences in Breathing Rate Before and After Exercise
Oxygen consumption also increases linearly with increasing work rate at submaximal intensities. The respiration rate may remain faster and deeper than normal for up to 40 minutes after the exercise ends.

How Does Exercise Affect The Rate Of Breathing Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Muscular endurance training has a greater reliance on oxygen for energy than hypertrophy training the work intervals are longer and the rest periods are shorter allowing a minimum of recovery so the response of the respiratory system is much.

. Compare the time it took the bromothymol blue solution to change color before exercise and after exercise. During exercise or after exercise you can monitor your heart rate. Intense exercise may increase the breathing rate up to 40 or 50 breaths per minute.
The subjects were separated into male and female to look for a difference between the genders breathing and heart rate. Click here to find your maximum heart beat based on the age and exercise intensity. A normal resting breathing rate is 15 breaths per minute.
The more oxygen your body needs to perform the exercise the higher your breathing and heart rate will be. Blood pH The pH of the blood is normally 735 to 745 a narrow range. Average and difference of pulse rate before and after exercising.
9 and post exercise 129. Gas Exchange During Exercise. Graph 2 also shows there is an increase in the heart rate after exercise.
The rate of heartbeat decreases as physical activity increases. As activity increases the heart rate will increase in speed. When you exercise and your muscles work harder your body uses more oxygen and produces more carbon dioxide.
After an exercise the heart rate gradually decrease and oxygen intake occurred at a normal level. Heart Rate is defined as the amount of times a persons heart beats in one minute. By contrast 13 of 19 studies in which final VO2 was 92-100 of highest VO2 were followed by relative rapid shallow breathing.
During exercise ventilation might increase from resting values of around 56 litre min 1 to 100 litre min 1. It may take 10-20 minutes post exercise for the breathing rate to return to normal with hypertrophy training because of this. Ventilation increases linearly with increases in work rate at submaximal exercise intensities.
Breathing rate breaths per minute At rest During exercise Immediately after exercise 2 min after exercise 4 min. While working out the target heart rate should be no more than 50 to 85 of your maximum heart beat. After anaerobic exercise your body takes longer to recover from that oxygen debt and your pulse may remain.
After they do some exercise record their rate of breathing every minute until it returns to the normal resting value. Explain the difference in question 2 What is the. However physically active people often have a lower heart rate than 60 while at rest.
A resting heart rate is the persons heart rate prior to any activity or exercise. At the onset of exercise the brain signals increases in heart and breathing rates in anticipation of the increased need for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange of exercise. So after exercise your heart rate will be higher but slowly even out as your body returns to homeostasis.
After 2 minutes adding this to your table. The ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen utilized increases due to. Breathing rate increases with in increase of physical activity.
Once exercise begins circulating levels of the hormone epinephrine also referred to as adrenaline increase. This increase stimulates ventilation as well. Although you havent begun to tax your muscles.
An increased heart rate is essential as it replaces oxygen in the muscles that is used during said activity and gets. During exercise your body will need more nutrients because your tissues are expending more. Exercise to improve aerobic fitness elevates the respiration rate but not as high as more intense exercises.
Figure 3 shows the aerobic exercise significantly increased the heart rate by 68 and the breathing rate by 58 imme- diately after the exercise compared to the nonexercise trials. The table also shows that two of the participants had the same increase in heart rate after exercise pic Graph 1 Mean difference in the increase of heart rate after exercise The median heart rate pre exercise was 77. 4 min after exercise.
Utilizing more oxygen implies you will likewise produce more carbon dioxide due to the increase in your metabolic rate. If you have a pulse meter you may be able to record pulse rate. Thus the heart pumped at a quicker rate to get this oxygen into its cells.
For the breathing rate I would say that exercise for 5 minutes would be better than 2 minutes as after 2 minutes the breathing rate did not go overly higher but after 5 minutes the breathing rate would have been a lot higher there for the time in which the breathing rate went back to normal would have took longer although this would not really change the results much. The hypothesis of the experiment sought to test whether there was a notice able difference in the effect of aerobic exercises between the pulse rates of athletes and non-athletes. Bromothymol blue is in indicator for carbon dioxide which means that it will change color if carbon dioxide is present.
When you exercise at high intensity youre in an anaerobic or oxygen-deprived state. In order to perform physical activity your muscles require oxygenated blood to circulate at an increased rate. While working out your body needs higher energy which implies your tissues utilize more oxygen than they do when at rest.
Hence breathing rate increased in order to get the blood oxygenated and get rid of this carbon dioxide. Heart ratebeats per minute At rest During exercise Immediately after exercise. Why Breathing Rates Increase Before Exercise.
There was no systematic difference between breathing pattern during exercise and recovery in tests where final O2 consumption VO2 was 45-92 of the subjects highest VO2. The rate of breathing increases as physical activity increases. 2 min after exercise.
Before exercise your normal heart rate supplies you body with sufficient Oxygen. To cope with this extra demand your breathing has to increase from about 15 times a minute 12 litres of air when you are resting up to about 4060 times a minute 100 litres of air during exercise. 57 is shown in graph 2.
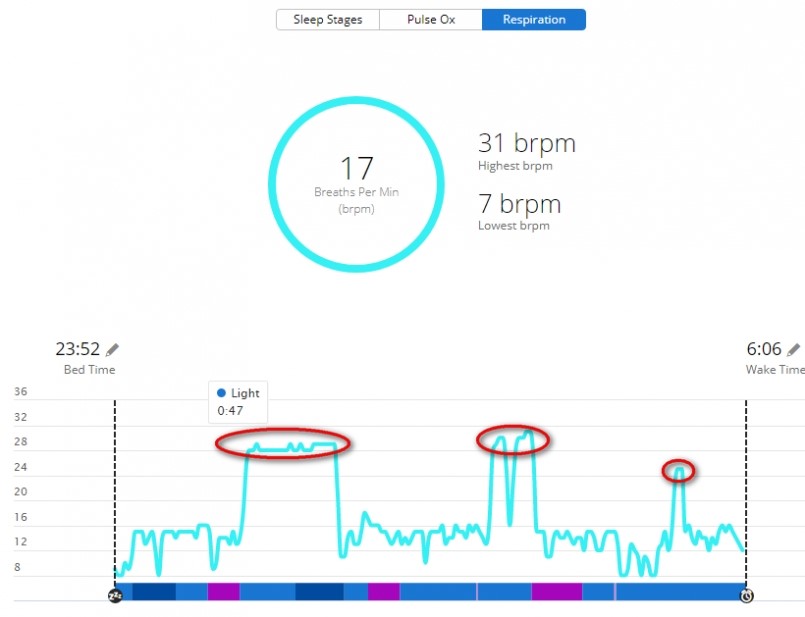
Critical Relationship Between Respiratory Rate Heart Rate And Cadence Garmin Blog

Critical Relationship Between Respiratory Rate Heart Rate And Cadence Garmin Blog
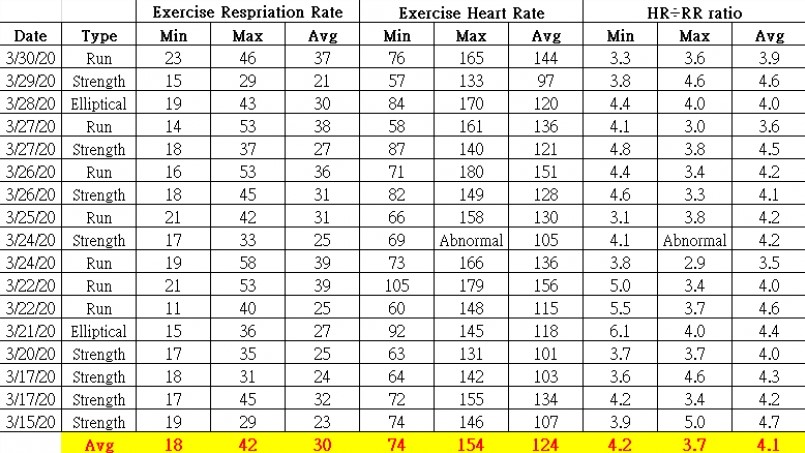
Critical Relationship Between Respiratory Rate Heart Rate And Cadence Garmin Blog
Comments
Post a Comment